Causes of knee extensor mechanism injuries
15th December 2021
Back to basics
10th January 2022In the event that an acute sickle cell crisis, the best place to be is an emergency department. However, many are unsure of the nature of sickle cell crises and how sickle cell crises are caused by sickle cell disease. Read on to learn about a sickle cell crisis occurring in the emergency department and how to respond appropriately.
What is sickle cell disease?
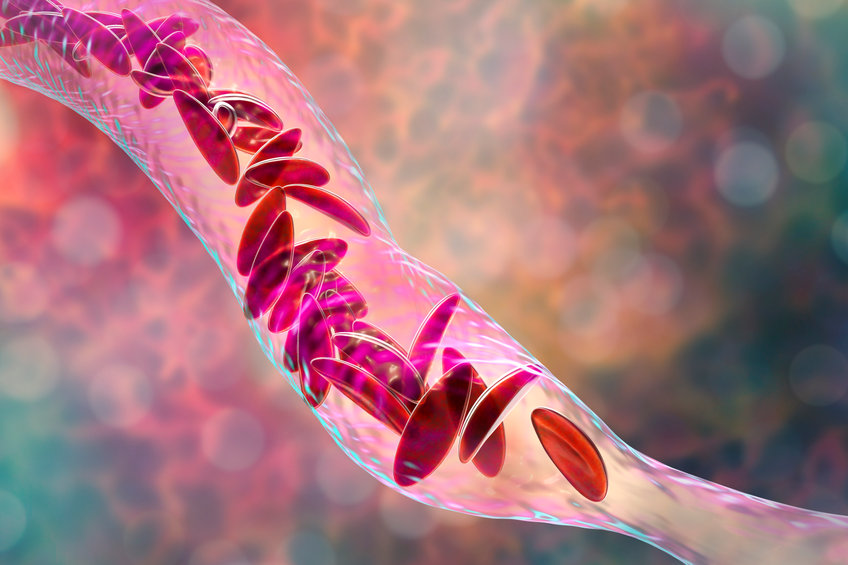
Sickle cell disease is an inherited red blood cell disorder. Named because it turns typically round red blood cells into hard and sticky sickle-shaped cells, sickle cell disease affects the longevity of impacted red blood cells and is a lifelong condition due to its inherited nature.
What are the symptoms of sickle cell disease?
Sickle cells disease has a range of symptoms with a range of permanence. Below are the most common sickle cell disease symptoms and their durations:
• Sickle cell crises, severe and painful episodes lasting up to a week as a result of red blood cell deficiency.
• Increased risk of serious infections. Rigid cells block and damage the spleen leading to increased susceptibility to infections in the long term. A damaged spleen has a permanent impact.
• Anaemia due to lesser oxygen circulation resulting in tiredness and shortness of breath.
• Increased chance of strokes resulting from reduced oxygen circulation through the bloodstream.
Sickle cell crises are the specific issues discussed in this piece and are the primary focus of the remainder of the article.
What is a sickle cell crisis?
The aforementioned period of extreme pain known as a sickle cell crisis is the most common symptom of sickle cell disease. A sickle cell crisis occurs when blood vessels to a part of the body are blocked by sickle cells. These vaso-occlusive episodes are responsible for 80% of hospital admissions and on average last for seven days.
How is a sickle cell crisis treated?
A sickle cell crisis is treated through strong analgesia. Due to the nature of the issue, painkillers are the only option as relieving the blockage is impossible. This is combined with high flow oxygen provision, increasing the proportion of oxygen inhaled as a response to the restriction of oxygen to the area caused by the sickle cell crisis.
Does the condition worsen?
Dependent on the nature of the sickle cell crisis, the impact on the patient’s wider health can worsen. For example in the event that the sickle cell crisis worsens oxygen flow to the brain, further action may be necessary for the prevention of more severe health issues such as a stroke. In these cases, urgent transfer from the emergency department to haematology or another relevant department is advised as the situation has the potential for severe escalation.
Aftercare for sickle cell crisis
In the event that a sickle cell crisis is resolved of its own accord, advise patients on appropriate aftercare provisions. These include eating a balanced diet and remaining hydrated and taking an iron-free multivitamin daily. Although sickle cells themselves are unavoidable, a healthier body is better prepared to resolve the side effects.