The Use of Tourniquets – An Ancient Technique Coming Back Into Use
29th May 2024
Why expert witnesses MUST be independent
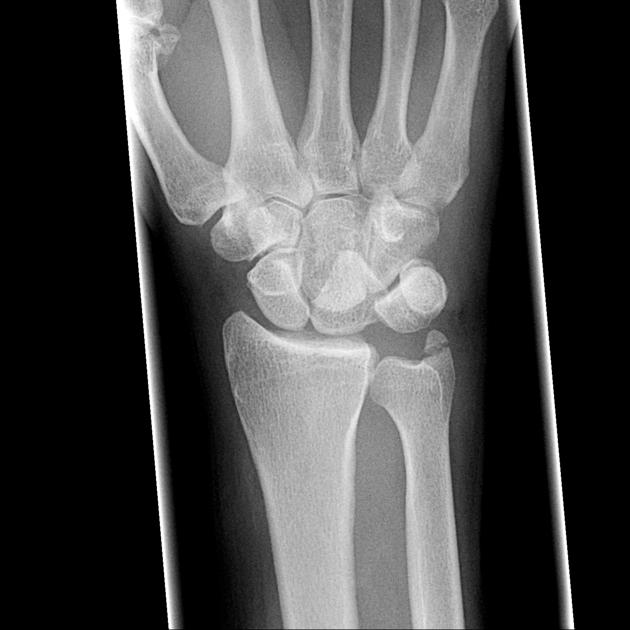
5th August 2024Some of the most frequent injuries in people who attend the emergency department are those that occur
to the wrist. A complex structure, the wrist comprises eight carpal bones as well as tendons and ligaments
which allow for a full range of movement. Due to its structural complexity, it can be susceptible to a variety
of different types of trauma, which may arise from falls, sport-related activities or even accidents at work.
While x-rays are typically used for initial assessment of such injuries, it can be difficult to diagnose certain
carpal bone injuries in this manner. Below, we take a look at what injuries could be present in a damaged
wrist, focusing on hamate fractures and lunate dislocations. Furthermore, we explain why these can be
difficult to see on x-rays and the implications that could arise from a delayed or missed diagnosis of such
an injury.
Carpal bones explained
The proximal row of carpal bones consist of the scaphoid, lunate and pisiform, while the distal row
contains the hamate, capitate, trapezoid and trapezium. As such, they articulate with each other
alongside the radius and ulna as well as the metacarpal bones of the hand. This working structure helps
to facilitate a wide range of wrist movements that can be impacted if any of these bones are damaged.
Here, we look at two specific injuries; the hamate fracture and the lunate dislocation, which could cause
significant problems in injured patients, particularly if missed or misdiagnosed.
Hamate fracture
As a hook shaped bone which is located on the little fingers side of the wrist, hamate fractures are
typically caused by a fall onto the outstretched hand, or a direct blow. The most common area in which
the bone is fractured is at the hook (hamulus). Due to the subtle appearance and the fact that the hamate
overlaps with other bones, hamate fractures are often missed on initial x-rays. Due to the hook’s
importance in attaching the tendons and ligaments that are involved in wrist and hand function, patients
are likely to experience issues with persistent pain, grip strength and weakness in the area.
Lunate dislocation
A crescent shaped bone which is located in the middle of the proximal carpal row, the lunate is vital for
proper wrist function. A lunate dislocation can, therefore, cause serious problems. Typically seen in high
energy traumas, such as car accidents and falls from height, they are classified into two separate
displacements; dorsal or volar.
Again, these are challenging injuries to diagnose on x-ray. This is particularly true in the emergency
department, where swelling of the soft tissues can obscure the bone displacement. However, a missed
diagnosis or late diagnosis of a lunate dislocation can be devastating to the patient. If the dislocation is to
the palmar ( volar ) side it is within he carpal tunnel and can compress the median nerve such that if the
dislocation is identified late can lead tyo long term symptoms of median nerve injury. It can also
compromise the blood supply to the lunate. This can, in complex cases, lead to vascular necrosis and
instability in the wrist.
How to avoid missed fractures
While these injuries can be difficult to diagnose, especially in a busy emergency department, it is crucial
that the standard of care provided to patients is upheld. Since delayed or missed diagnosis of these
significant injuries can lead to the impairment of function of the wrist as well as potential long-term
disabilities, it is vital that medical professionals consider the suspicion of these injuries, particularly where
the patient has a history of trauma and wrist pain. It is important to have the X-rays reviewed early by a
radiologist even if the initial clinicla diagnosis is missed by the Emergency Medicine team. Using
advanced imaging, including MRI and CT scans may be prudent, to confirm or refute the diagnosis but
will normally be arranged after referral to the orthopaedic team. This will allow the physician to initiate the
proper treatment protocol quickly.